R is:
You can install R from the following two sources:
CRAN Website: http://cran.r-project.org/
RStudio: https://www.rstudio.com/products/rstudio/download/
R Installation:
First, you will learn how to install R on Windows from the CRAN website. You can download the package from: https://cran.r-project.org/bin/windows/base/.
In RStudio, you can set the workspace by clicking Tools -> Global Options.
R has many operators to perform different mathematical and logical operations. These can be categorized as follows:
Arithmetic Operators: used for mathematical operations like addition and multiplication, look at the table below:
- A programing language developed at AT&T Bell Laboratories by Robert Gentleman and Ross Ihaka
- An alternative to S language
- A free, open source language, with highly active community members
- Available across all platforms (Linux, Mac, Windows)
- The RStudio program can run on a desktop or through a web browser.
You can install R from the following two sources:
CRAN Website: http://cran.r-project.org/
RStudio: https://www.rstudio.com/products/rstudio/download/
R Installation:
First, you will learn how to install R on Windows from the CRAN website. You can download the package from: https://cran.r-project.org/bin/windows/base/.
- Download R 3.X.X for Windows executable file (.exe).
- Click “Next” in the Setup Wizard. (You may leave the setting as default.)
- Finally, open R console (RGUI from your desktop).
- Download RStudio from https://www.rstudio.com/products/rstudio/download/.
- Run the installation file.
- Open RStudio.
In RStudio, you can set the workspace by clicking Tools -> Global Options.
- getwd() -return working directory
- setwd() -set working directory
Many data scientist programmers and statisticians use R to design tools for analyzing data and to contribute their codes as pre-assembled collections of functions and objects called packages. You can install an R package by clicking GUI RStudio ->Tools -> Install Packages or directly from packages tab in File/Package Panel
Getting Started : Quick Tour!!
R has many operators to perform different mathematical and logical operations. These can be categorized as follows:
Arithmetic Operators: used for mathematical operations like addition and multiplication, look at the table below:
Operator
|
Description
|
+
|
Addition
|
-
|
Subtraction
|
*
|
Multiplication
|
/
|
Division
|
^
|
Exponent
|
%%
|
Modulus
|
%/%
|
Integer Division
|
Logical Operators: These operators are used to perform Boolean operations such as “AND” and “OR.”, look at the table below:
Relational Operators: used to compare two values, look at the table below:
Assignment Operator: These operators are used to assign values to variables. Variables are assigned using “<-”, although “=” also works.
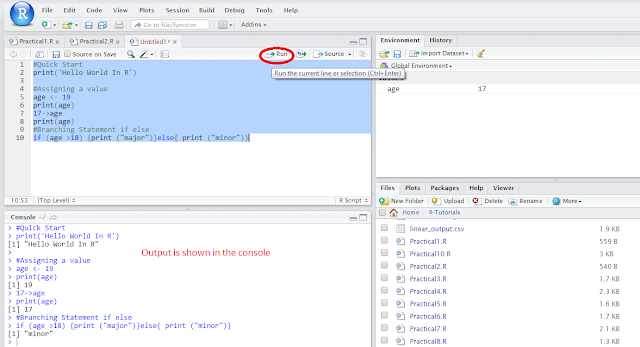
Lets do a simply hello world program and execute as below.
Operator
|
Description
|
!
|
Logical NOT
|
&
|
Element-wise logical AND
|
&&
|
Logical AND
|
|
|
Element-wise logical OR
|
||
|
Logical OR
|
Operator
|
Description
|
<
|
Less than
|
>
|
Greater than
|
<=
|
Less than or equal to
|
>=
|
Greater than or equal to
|
==
|
Equal to
|
!=
|
Not equal to
|
Lets do a simply hello world program and execute as below.



No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.